
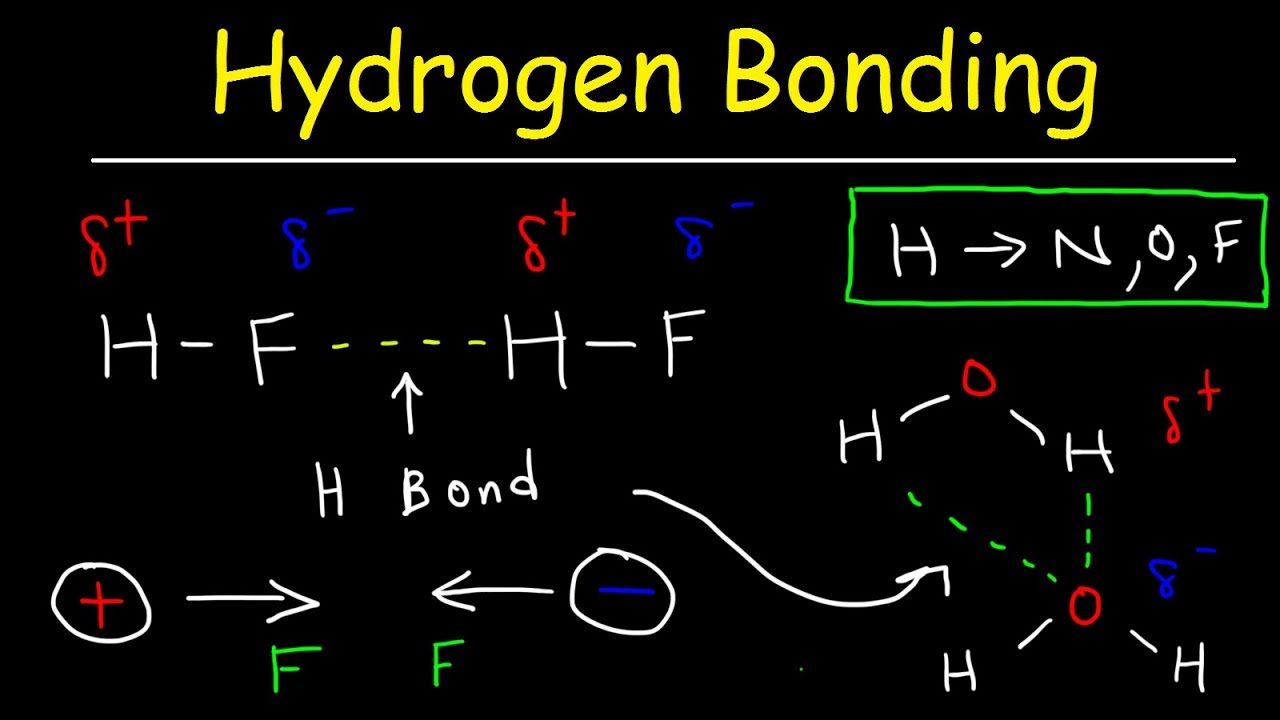
Higher boiling point than similar molecules (HCl, HBr, HI) containing elements of the same group of the Periodic Table,īut heavier and less electronegative. Hydrogen bond between two water moleculesīecause of the extensive network of hydrogen bonds between molecules, HF has a In electronegativity between H and F, a hydrogen bond occurs between the hydrogen atom of a molecule and the Hydrogen fluoride is composed of HF molecules. Hydrogen atoms in white, Fluorine atoms in green Polar substances like hydrogen fluoride and water. All together, they play a central role in determining the chemical and physical properties of A single hydrogen bond is relatively weak: usually, however, a high number of suchīonds forms simultaneously. The hydrogen atom is aligned with the two electronegative atoms. Hydrogen bond is a directional bond, meaning that it is stronger when It interacts with the negative end of a neighboring molecule,įorming a "bridge" between the two molecules. The hydrogen atom is the positive end of the molecule. Δ +) on one side and a partial negative charge (δ -) on the opposite The molecule, though it is electrically neutral, has a partial positive charge (indicated as When a hydrogen atom is bound to a strongly electronegative atom, a charge The bond isĬommonly represented as a dotted line between the hydrogen atom and the other electronegative atom, as shown in theįigure. Hydrogen bond Hydrogen bond is a special type of interaction between molecules: it forms wheneverĪ hydrogen atom, bound to a strongly electronegative (able to attract electrons) atom, at the same time interacts withĪnother strongly electronegative atom having a lone pair of electrons, like oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine. CONTENTS | Comments and contacts | Credits


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
